Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
| Nerve: Phrenic nerve | ||
|---|---|---|
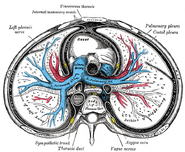
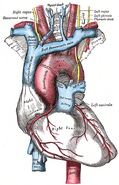
| The phrenic nerve and its relations with the vagus nerve. (Phrenic labeled at upper left.) | ||
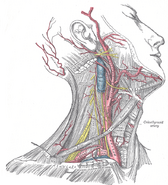
| Plan of the cervical plexus. (Phrenic labeled at bottom right.) | ||
| Latin | nervus phrenicus | |
| Gray's | subject #210 928 | |
| Innervates | ||
| From | C3-C5 of cervical plexus | |
| To | ||
| MeSH | [1] | |
The phrenic nerve arises from the third, fourth, and fifth cervical spinal nerves (C3-C5) in humans. It arises from the fifth, sixth and seventh cervical spinal nerves (C5-7) in most domestic animals.
Function[]
The phrenic nerve is made up mostly of motor nerve fibres for producing contractions of the diaphragm. In addition, it provides sensory innervation for many components of the mediastinum and pleura, as well as the upper abdomen, especially the liver and gall bladder.
Path[]
Both phrenic nerves run from C3, C4 and C5 along the anterior scalene muscle deep to the carotid sheath.
- The right phrenic nerve passes over the right brachiocephalic artery, the subclavian vein, and the superior vena cava and then crosses the root of the right lung and then leaves the thorax by passing through the vena cava hiatus opening in the diaphragm at the level of T8. The right phrenic nerve passes over the right atrium.
- The left phrenic nerve passes over the left ventricle and pierces the diaphragm separately.
Both these nerves supply motor fibres to the diaphragm and sensory fibres to the fibrous pericardium, mediastinal pleura and diaphragmatic peritoneum.
The pericardiacophrenic artery and vein(s) travel with the phrenic nerve.
Clinical relevance[]
Pain arising from structures served by the phrenic nerve is often "referred" to other somatic regions served by spinal nerves C3-C5. For example, a subphrenic abscess (beneath the diaphragm) might cause a patient to feel pain in the right shoulder.
Irritation of the phrenic nerve (or the tissues supplied by it) leads to the hiccup reflex. A hiccup is a spasmodic contraction of the diaphram, which pulls air against the closed folds of the larynx.
The phrenic nerve must be identified during thoracic surgery and preserved. It passes anterior to the hilum of the corresponding lung, and therefore can be identified easily. Severing the phrenic nerve will paralyse that half of the diaphragm. Breathing will be made more difficult but will continue provided the other nerve is intact.
Additional images[]
External link[]
- GPnotebook -1402273763
- Dictionary at eMedicine Phrenic+nerve
- SUNY Figs 19:04-05 - "Left side of the mediastinum."
- SUNY Figs 25:03-15 - "Diagram of the cervical plexus."
| Nerves of head and neck: the cervical plexus |
|---|
| superficial: (lesser occipital - greater auricular - transverse cervical - supraclavicular) - deep: (ansa cervicalis - phrenic) |
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |