mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
*[[Area TG of Bonin-1947]] |
*[[Area TG of Bonin-1947]] |
||
*[[Brain]] |
*[[Brain]] |
||
| − | *[[ |
+ | *[[Lobe (anatomy)]] |
*[[Hippocampus]] |
*[[Hippocampus]] |
||
*[[Temporal lobe epilepsy]] |
*[[Temporal lobe epilepsy]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | ==Further reading== |
||
| + | * Kensinger, E. A., Ullman, M. T., & Corkin, S. (2001). Bilateral medial temporal lobe damage does not affect lexical or grammatical processing: Evidence from amnesic patient H.M. ''Hippocampus, 11,'' 337-346. [http://web.mit.edu/bnl/pdf/Kensinger%20et%20al.,%202001.pdf Full text] |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
Revision as of 00:47, 7 September 2009
| Brain: Medial temporal lobe | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:{{{Image}}}|250px|center|]] | ||
| {{{Caption}}} | ||
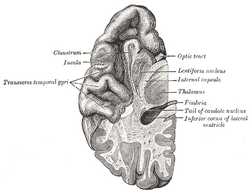
| Section of brain showing upper surface of temporal lobe. | ||
| Latin | lobus temporalis | |
| Gray's | subject #189 823 | |
| Part of | Brain | |
| Components | ||
| Artery | Middle cerebral and Posterior cerebral | |
| Vein | ||
| BrainInfo/UW | hier-107 | |
| MeSH | A08.186.211.730.885.213.863 | |
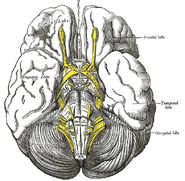
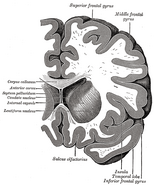
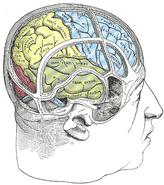
The temporal lobes are part of the cerebrum. They lie at the sides of the brain, beneath the lateral or Sylvian fissure. Seen in profile, the human brain looks something like a boxing glove. The temporal lobes are where the thumbs would be.
The temporal lobe is involved in auditory processing and is home to the primary auditory cortex. It is also heavily involved in semantics both in speech and vision. The temporal lobe contains the hippocampus and is therefore involved in memory formation as well.
Function
The superior temporal gyrus includes an area (within the Sylvian fissure) where auditory signals from the cochlea (relayed via several subcortical nuclei) first reach the cerebral cortex. This part of the cortex (primary auditory cortex) is involved in hearing. Adjacent areas in the superior, posterior and lateral parts of the temporal lobes are involved in high-level auditory processing. In humans this includes speech, for which the left temporal lobe in particular seems to be specialized. Wernicke's area, which spans the region between temporal and parietal lobes, plays a key role (in tandem with Broca's area, which is in the frontal lobe). The functions of the left temporal lobe are not limited to low-level perception but extend to comprehension, naming, verbal memory and other language functions. Sound processing is controlled by the temporal lobes- in the Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area.
The underside (ventral) part of the temporal cortices appear to be involved in high-level visual processing of complex stimuli such as faces (fusiform gyrus) and scenes (parahippocampal gyrus). Anterior parts of this ventral stream for visual processing are involved in object perception and recognition.
The medial temporal lobes (near the Sagittal plane that divides left and right cerebral hemispheres) are thought to be involved in episodic/declarative memory. Deep inside the medial temporal lobes, the hippocampi seem to be particularly important for memory function - particularly transference from short to long term memory and control of spatial memory and behavior.
Additional images
See Also
- Lobes of the brain
- Area TG of Bonin-1947
- Brain
- Lobe (anatomy)
- Hippocampus
- Temporal lobe epilepsy
Further reading
- Kensinger, E. A., Ullman, M. T., & Corkin, S. (2001). Bilateral medial temporal lobe damage does not affect lexical or grammatical processing: Evidence from amnesic patient H.M. Hippocampus, 11, 337-346. Full text
External links