Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Clinical: Approaches · Group therapy · Techniques · Types of problem · Areas of specialism · Taxonomies · Therapeutic issues · Modes of delivery · Model translation project · Personal experiences ·
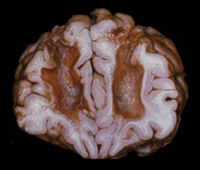
A human brain that had undergone leukotomy.
A leukotomy refers to what is now more commonly known as a prefrontal lobotomy (Greek: leuko: white matter of brain, tomy: cutting). It consists of cutting the connections to and from, or simply destroying, the prefrontal cortex. These procedures often result in major personality changes. For an example of the personality changes associated with damage to the frontal lobe not related to a surgical leukotomy, see the famous case of Phineas Gage.
History[]
The first human leukotomy was performed by the Portuguese physician and neurologist António Egas Moniz in 1936. He won the Nobel Prize for medicine in 1949 for this work.
The procedure was popularized in the United States by Dr. Walter Freeman, who traveled the country performing "ice pick lobotomies" on patients with psychiatric disorders. Eventually he began performing this procedure on anyone who wished to have one.
With the advent of Thorazine in the 1950s, leukotomy became more criticized, on charges of it being a kind of numbless torture destroying consciousness. Walter Freeman's services fell out of fashion, and he eventually lost his medical license when one of his patients died.
In 1977, the US Congress created a National Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research to investigate allegations that psychosurgery, including lobotomy techniques, was used to control minorities and restrain individual rights, and that it had unethical after-effects. It concluded that, in general, psychosurgery had positive effects. However, concerns about leukotomy steadily grew, some countries such as Germany, Japan and several US states prohibited it. Leukotomy was legally practiced in controlled and regulated US centers, and in Finland, Sweden, the United Kingdom, Spain, India, Belgium and the Netherlands. The practice had generally ceased by the early 1970s, but some countries continued small scale operations through the late 1980s. In France, 32 lobotomies were performed between 1980 and 1986 according to a IGAS report; about 15 each year in the UK, 70 in Belgium, and about 15 for the Massachusetts General Hospital of Boston.[1]
Lobotomies in Popular Culture[]
- Lobotomies, Thorazine and other things related to the mentally ill have also been referred on numerous occasions in punk and grunge rock. The first incident of such references is thought to have originated with The Ramones, when Joey was inspired to write songs by his brief stay in a New York psychiatric facility, manifested in such songs as: Teenage Lobotomy, Psycho Therapy, Gimme Gimme Shock Treatment etc.
- The song "Downer", by Nirvana, includes a line "hand out lobotomies to save little families".
- In the film Total Recall, lobotomies are given to people who suffer "schizoid embolisms" duing their virtual reality tours.
- US Comic songwriter Tom Lehrer mentioned on his An Evening Wasted With Tom Lehrer album that 'the nicest gift he had received this Christmas was a gift certificate, good at any hospital, for a lobotomy'.
- In the novel One Flew Over the Cuckoo's Nest, Randle McMurphy receives a lobotomy after he explodes into a violent rage towards the head nurse. The book was based on Ken Kesey's experience in a mental hospital in Northern Oregon. A film version was also made in 1975.
- Frances (1982)
- In Hannibal (2001), Hannibal Lecter gives a victim (Ray Liotta) a live lobotomy, cooks the salvaged parts of the brain, and feeds them to the victim.
- In a Simpsons Episode Ned Flanders uses lobotomies as a means of public control.
- In the 1958 Tennessee Williams play (and 1959 movie) Suddenly, Last Summer, which is set in 1937, Catherine (played in the movie by Elizabeth Taylor) is supposed to undergo a lobotomy to silence her, because she witnessed the violent murder of her cousin Sebastian and knows about his homosexuality.
- The iconic Iron Maiden mascot Eddie the Head was lobotmized during a live concert.
- Allen Ginsberg once stood on the steps outside the U.S. Capitol building, demanding a lobotomy until he was eventually led away. [citation needed]
- Max attempts to give himself a lobotomy in the film Pi by using a drill.
- In the computer game World of Warcraft, a dagger is named the Lobotomizer.
- The band Sepultura has a song called Lobotomy, from the album Morbid Visions
See also[]
- Psychosurgery -- Brain surgery intended to treat or alleviate severe mental illness.
Notes[]
- ^ includeonly>"La neurochirurgie fonctionnelle d'affections psychiatriques sévères", Comité Consultatif National d'Ethique, April 25, 2002.
External links[]
de:Lobotomie nl:Lobotomie pt:Lobotomia ru:Лоботомия
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |