| Nerve: Glossopharyngeal nerve | ||
|---|---|---|
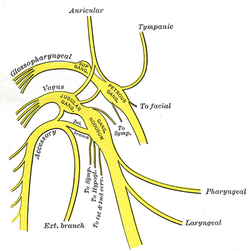
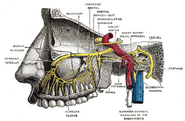
| Plan of upper portions of glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. | ||
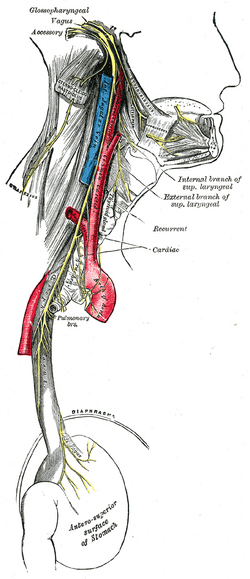
| Course and distribution of the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. (Label for glossopharyngeal is at upper right.) | ||
| Latin | nervus glossopharyngeus | |
| Gray's | subject #204 906 | |
| Innervates | stylopharyngeus | |
| From | ||
| To | tympanic nerve | |
| MeSH | A08.800.800.120.290 | |
The glossopharyngeal nerve is the ninth of twelve cranial nerves. It exits the brainstem out from the sides of the upper medulla, just rostral (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve.
| Cranial Nerves |
|---|
| CN 0 - Cranial nerve zero |
| CN I - Olfactory |
| CN II - Optic |
| CN III - Oculomotor |
| CN IV - Trochlear |
| CN V - Trigeminal |
| CN VI - Abducens |
| CN VII - Facial |
| CN VIII - Vestibulocochlear |
| CN IX - Glossopharyngeal |
| CN X - Vagus |
| CN XI - Accessory |
| CN XII - Hypoglossal |
Functions
There are a number of functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve:
- It receives sensory fibres from the posterior one-third of the tongue, the tonsils, the pharynx, the middle ear and the carotid body.
- It supplies parasympathetic fibres to the parotid gland via the otic ganglion.
- It supplies motor fibres to stylopharyngeus muscle
- It contributes to the pharyngeal plexus.
Brainstem connections
The glossopharyngeal nerve, being mostly sensory, does not have a cranial nerve nucleus of its own. Instead it must project into many different structures in the brainstem:
- Solitary nucleus: Taste from the posterior one-third of the tongue and information from carotid baroreceptors and carotid body chemoreceptors
- Spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve: Visceral pain as well as somatic sensory fibers from the skin of the outer ear.
- Nucleus ambiguus: The lower motor neurons for the stylopharyngeus muscle.
- Inferior salivatory nucleus: Parasympathetic input to the parotid and mucous glands.
Path
From the medulla oblongata, the glossopharyngeal nerve passes laterally across the flocculus, and leaves the skull through the central part of the jugular foramen, in a separate sheath of the dura mater, lateral to and in front of the vagus and accessory nerves.
In its passage through the jugular foramen, it grooves the lower border of the petrous part of the temporal bone; and, at its exit from the skull, passes forward between the internal jugular vein and internal carotid artery; it descends in front of the latter vessel, and beneath the styloid process and the muscles connected with it, to the lower border of the stylopharyngeus.
It then curves forward, forming an arch on the side of the neck and lying upon the stylopharyngeus and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle.
From there it passes under cover of the hyoglossus muscle, and is finally distributed to the palatine tonsil, the mucous membrane of the fauces and base of the tongue, and the mucous glands of the mouth.
Testing the glossopharyngeal nerve
The gag reflex is absent in patients with damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve as it is responsible for the afferent limb of the reflex.
Additional images
External links
- BrainInfo at the University of Washington hier-698
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cn9.htm
- MedlinePlus Image 9350
- Norman/Georgetown cranialnerves (IX)
I-IV: olfactory - optic - oculomotor - trochlear
V: trigeminal: trigeminal ganglion
V1: ophthalmic: lacrimal - frontal (supratrochlear, supraorbital) - nasociliary (long root of ciliary, long ciliary, infratrochlear, posterior ethmoidal, anterior ethmoidal) - ciliary ganglion (short ciliary)
V2: maxillary: middle meningeal - in the pterygopalatine fossa (zygomatic, zygomaticotemporal, zygomaticofacial, sphenopalatine, posterior superior alveolar)
in the infraorbital canal/infraorbital nerve (middle superior alveolar, anterior superior alveolar)
on the face (inferior palpebral, external nasal, superior labial, infraorbital plexus) - pterygopalatine ganglion (deep petrosal, nerve of pterygoid canal)
branches of distribution (palatine, nasopalatine, pharyngeal)
V3: mandibular: nervus spinosus - medial pterygoid - anterior (masseteric, deep temporal, buccal, lateral pterygoid)
posterior (auriculotemporal, lingual, inferior alveolar, mylohyoid, mental) - otic ganglion - submandibular ganglion
VI: abducens
VII: facial: nervus intermedius - geniculate - inside facial canal (greater petrosal, nerve to the stapedius, chorda tympani)
at exit from stylomastoid foramen (posterior auricular, digastric - stylohyoid)
on face (temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical)
VIII: vestibulocochlear: cochlear (striae medullares, lateral lemniscus) - vestibular
IX: glossopharyngeal: fasciculus solitarius - nucleus ambiguus - ganglia (superior, petrous) - tympanic - carotid sinus
X: vagus: ganglia (jugular, nodose) - Alderman's nerve - in the neck (pharyngeal branch, superior laryngeal ext and int, recurrent laryngeal)
in the thorax (pulmonary branches, esophageal plexus) - in the abdomen (gastric plexuses, celiac plexus, gastric plexus)
XI: accessory XII: hypoglossal
de:Nervus glossopharyngeus lt:Liežuvinis ryklės nervas nl:Nervus glossopharyngeus no:Nervus glossopharyngeus pt:Nervo glossofaríngeo
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |