No edit summary |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{BioPsy}} |
{{BioPsy}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | For list of ganglia see: [[Ganglia (disambiguation)]] |
||
| − | In vertebrate anatomy, a '''ganglion''' is a [[biological tissue|tissue]] mass that contains the [[dendrite]]s and cell bodies (or "somata") of [[neuron|nerve cell]]s, in most case ones belonging to the [[PNS|peripheral nervous system]]. Within the [[central nervous system]] such a mass is often called a [[nucleus (neuroanatomy)|nucleus]]. An interconnected group of ganglia is called a [[plexus]]. |
||
| + | In [[anatomy]], a '''ganglion''' (plural '''ganglia''') is a [[biological tissue|tissue mass]].<ref>{{DorlandsDict|four/000043442|ganglion}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | Cells found in a ganglion are called [[ganglion cell]]s, though this term is also sometimes used to refer specifically to [[Retinal ganglion cell]]s. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | == |
+ | ==Neurology== |
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | In neurological contexts, ganglia are composed mainly of [[Soma (biology)|somata]] and [[dendrite|dendritic structures]] that often interconnect with other ganglia to form a complex system of ganglia known as a [[plexus]]. Ganglia provide relay points and intermediary connections between different neurological structures in the body, such as the [[peripheral nervous system|peripheral]] and [[central nervous system|central]] nervous systems. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | There are two major groups of ganglia: |
||
| + | * [[dorsal root ganglion|dorsal root ganglia]] (also known as the spinal ganglia) - contain the cell bodies of [[Afferent nerve|sensory (afferent)]] [[nerve]]s |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | ===Basal ganglia=== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | The term "ganglion" usually refers to the [[peripheral nervous system]]. <ref name="titleUNSW Embryology- Glossary G">{{cite web |url=http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/Index/G.htm |title=UNSW Embryology- Glossary G |accessdate=2008-01-13 |format= |work=}}</ref> |
||
| + | |||
| + | However, in the brain (part of the [[central nervous system]]), the "[[basal ganglia]]" is a group of nuclei interconnected with the [[cerebral cortex]], [[thalamus]] and [[brainstem]], associated with a variety of functions: motor control, cognition, emotions and learning. |
||
| + | |||
| + | Partly due to this ambiguity, the [[Terminologia Anatomica]] recommends using the term "basal nuclei" instead of "basal ganglia". |
||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == |
||
| + | * [[Ganglion blocking agents]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | * [[Ganglion cyst]] |
||
| + | * [[Ganglionectomy]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | * [[Spinal ganglia]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== |
||
| + | {{reflist}} |
||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Autonomic nervous system]] |
||
[[Category:Central nervous system]] |
[[Category:Central nervous system]] |
||
| + | [[[CAtegory:Ganglia]] |
||
| + | [[Category:Medical terms]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Peripheral nervous system]] |
[[Category:Peripheral nervous system]] |
||
| + | <!-- |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | [[es:Ganglio nervioso]] |
||
| + | [[fr:Ganglion nerveux]] |
||
| + | [[it:Ganglio]] |
||
| + | [[he:גנגליון]] |
||
| + | [[mk:Ганглија]] |
||
| + | [[nl:Zenuwknoop]] |
||
| + | [[ja:神経節]] |
||
| + | [[no:Ganglion]] |
||
| + | [[nds:Ganglion]] |
||
| + | [[pl:Zwój (anatomia)]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | [[ru:Ганглий]] |
||
| + | [[sr:Ганглион]] |
||
| + | [[fi:Hermosolmu]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | [[tg:Гангли]] |
||
| + | [[ur:کتلہ]] |
||
| + | --> |
||
{{enWP| Ganglion}} |
{{enWP| Ganglion}} |
||
Latest revision as of 06:05, 23 August 2012
Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
For list of ganglia see: Ganglia (disambiguation)
In anatomy, a ganglion (plural ganglia) is a tissue mass.[1]
Cells found in a ganglion are called ganglion cells, though this term is also sometimes used to refer specifically to Retinal ganglion cells.
Neurology
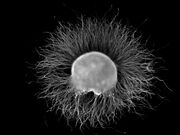
This is a dorsal root ganglion (DRG) from a chicken embryo (around stage of day 7) after incubation overnight in NGF growth medium stained with anti-neurofilament antibody. Note the axons growing out of the ganglion.
In neurological contexts, ganglia are composed mainly of somata and dendritic structures that often interconnect with other ganglia to form a complex system of ganglia known as a plexus. Ganglia provide relay points and intermediary connections between different neurological structures in the body, such as the peripheral and central nervous systems.
There are two major groups of ganglia:
- dorsal root ganglia (also known as the spinal ganglia) - contain the cell bodies of sensory (afferent) nerves
- autonomic ganglia - contain the cell bodies of autonomic nerves.
In the autonomic nervous system, fibers from the central nervous system to the ganglia are known as preganglionic fibers, while those from the ganglia to the effector organ are called postganglionic fibers.
Basal ganglia
The term "ganglion" usually refers to the peripheral nervous system. [2]
However, in the brain (part of the central nervous system), the "basal ganglia" is a group of nuclei interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and brainstem, associated with a variety of functions: motor control, cognition, emotions and learning.
Partly due to this ambiguity, the Terminologia Anatomica recommends using the term "basal nuclei" instead of "basal ganglia".
See also
- Ganglion blocking agents
- Ganglion cell
- Ganglion cyst
- Ganglionectomy
- Nervous system
- Neuron
- Spinal ganglia
References
- ↑ Template:DorlandsDict
- ↑ UNSW Embryology- Glossary G. URL accessed on 2008-01-13.
[[[CAtegory:Ganglia]]
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |