Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
|
Dihydrotestosterone chemical structure | |
IUPAC name | |
| CAS number 521-18-6 |
ATC code A14ciAA01 |
| PubChem 10635 |
DrugBank [1] |
| Chemical formula | {{{chemical_formula}}} |
| Molecular weight | 290.440 g/mol |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Legal status | |
| Routes of administration | |
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) (Full name: 5α-Dihydrotestosterone, abbreviating to 5α-DHT; INN: androstanolone) is a biologically active metabolite of the hormone testosterone, formed primarily in the prostate gland, testes, hair follicles, and adrenal glands by the enzyme 5α-reductase by means of reducing the 4,5 double-bond. Dihydrotestosterone belongs to the class of compounds called androgens, also commonly called androgenic hormones or testoids. Androgens are part of the biology of gender by stimulating and controling the development and maintenance of masculine characteristics. DHT is thought to be approximately 30 times more potent[How to reference and link to summary or text] than testosterone because of increased affinity for the androgen receptor.
Significance[]
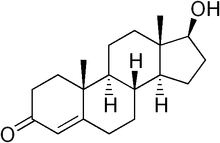
Testosterone. Note the major difference -- the 4,5 double-bond on the A (leftmost) ring.
DHT is produced by males in utero and is responsible for the formation of male gender specific characteristics. DHT is also an important contributor to other characteristics generally attributed to males, including facial and body hair growth, and deepening of the voice. DHT has been shown to be deactivated in skeletal muscle through the actions of 3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and therefore does not have a significant effect on muscle hypertrophy.
Pathology[]
It is suspected that DHT is the primary contributing factor in most cases of male-pattern baldness. Women with increased levels of DHT may develop certain androgynous male secondary sex characteristics, including a deepened voice and facial hair. DHT also seems to play a role in the development or exacerbation of benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH, and prostate cancer, though the exact reason for this is not known.
DHT is also known to participate in the development of acne.
Treatment[]
A natural substance known to control DHT is zinc. However, zinc is also an aromatase inhibitor which indirectly increases testosterone. This can decrease the anti-dht effects. In fact, zinc is even recommended for low testosterone levels.[How to reference and link to summary or text]
The drugs belonging to the group known as 5α-reductase inhibitors are used for treatment of problems stemming from DHT. This group includes finasteride (sold under the names Proscar for BPH and Propecia for androgenic alopecia as well as in generic formulation) and dutasteride (sold under the name Avodart). Currently, DHT supplementation is not used as a treatment for DHT/androgen deficiency.
Alternative treatments used to inhibit DHT include dietary supplementation with, or topically administered preparations of, saw palmetto berry extractives. Unlike most known 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, saw palmetto induces its effects without interfering with the cellular capacity to secrete PSA. [2] Saw palmetto extract has been demonstrated to inhibit both isoforms of 5-alpha-reductase unlike finasteride which only inhibits the (predominant) type 2 isoenzyme of 5-alpha-reductase. [3] [4] [5] [6]
The chemical equol, derived by consuming foods rich in soy isoflavones by persons with certain digestive-tract bacterial flora, appears to have an androgen-inhibitive effect.
Green tea, in many studies, has been found a potent DHT inhibitor. However, in one trial using mice, both the testosterone and DHT levels increased. However, if the isoflavones in soy are also ingested, the green tea has a synergetic decreasing effect on DHT.
Anabolic steroids (A14) (trademark names in brackets) | |
|---|---|
| Androstan (carbon 19 present) |
Androstadienone • Boldenone undecylenate (Equipoise) • Desoxymethyltestosterone (Madol) • DHT • Methandrostenolone (Dianabol) • Methenolone • Norethandrolone • Oxandrolone (Anavar) • Oxymetholone (Anadrol) • Quinbolone (Anabolicum Vister) • Stanozolol (Winstrol) • Testosterone • Clostebol • 4-Chlordehydromethyltestosterone (Turinabol) • Fluoxymesterone (Halotestin) • Drostanolone (Masteron) • DHEA • Oxymetholone (Anadrol-50) • Mesterolone (Proviron) • Methenolone enanthate (Primobolan) • Mestanolone |
| Estren (carbon 19 absent) |
Ethylestrenol • Nandrolone (Deca Durabolin) • Norbolethone (Genabol) • Oxabolone cipionate • Trenbolone (Fina) • Mibolerone (Cheque Drops) • Tetrahydrogestrinone (The Clear) |
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |