Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
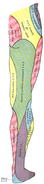
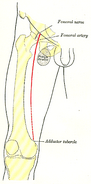
| Nerve: Femoral nerve | ||
|---|---|---|
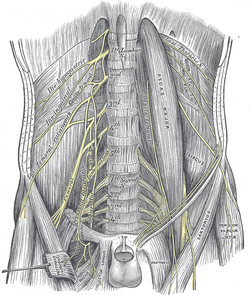
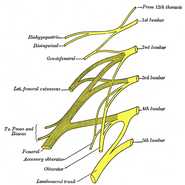
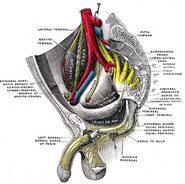
| The lumbar plexus and its branches. (Femoral labeled at bottom left.) | ||
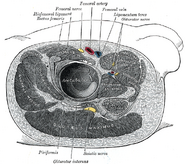
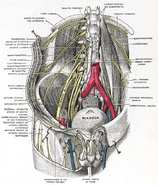
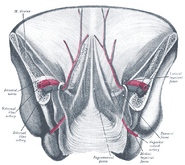
| Femoral sheath laid open to show its three compartments. (Femoral nerve visible in yellow.) | ||
| Latin | nervus femoralis | |
| Gray's | subject #212 955 | |
| Innervates | anterior compartment of thigh | |
| From | ||
| To | ||
| MeSH | A08.800.800.720.450.250 | |
- Main article: Spinal nerves
The femoral nerve, the largest branch of the lumbar plexus, arises from the dorsal divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves. It descends through the fibers of the Psoas major, emerging from the muscle at the lower part of its lateral border, and passes down between it and the Iliacus, behind the iliac fascia; it then runs beneath the inguinal ligament, into the thigh, and splits into an anterior and a posterior division. Under the inguinal ligament, it is separated from the femoral artery by a portion of the Psoas major.
In the abdomen[]
Within the abdomen the femoral nerve gives off small branches to the Iliacus, and a branch which is distributed upon the upper part of the femoral artery; the latter branch may arise in the thigh.
In the thigh[]
Anterior division[]
In the thigh the anterior division of the femoral nerve gives off anterior cutaneous and muscular branches.
- Anterior cutaneous branches: The anterior cutaneous branches comprise the following nerves: intermediate cutaneous nerve and medial cutaneous nerve.
- Muscular branches (rami musculares): The nerve to the Pectineus arises immediately below the inguinal ligament, and passes behind the femoral sheath to enter the anterior surface of the muscle; it is often duplicated. The nerve to the Sartorius arises in common with the intermediate cutaneous.
Posterior division[]
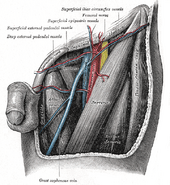
The posterior division of the femoral nerve gives off the saphenous nerve, and muscular and articular branches.
- The saphenous nerve (n. saphenus; long or internal saphenous nerve) is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve.
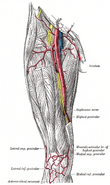
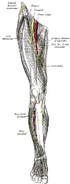
- The muscular branches supply the four parts of the Quadriceps femoris.
- The branch to the Rectus femoris enters the upper part of the deep surface of the muscle, and supplies a filament to the hip-joint.
- The branch to the Vastus lateralis, of large size, accompanies the descending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex artery to the lower part of the muscle. It gives off an articular filament to the knee-joint.
- The branch to the Vastus medialis descends lateral to the femoral vessels in company with the saphenous nerve. It enters the muscle about its middle, and gives off a filament, which can usually be traced downward, on the surface of the muscle, to the knee-joint.
- The branches to the Vastus intermedius, two or three in number, enter the anterior surface of the muscle about the middle of the thigh; a filament from one of these descends through the muscle to the Articularis genu and the knee-joint. The articular branch to the hip-joint is derived from the nerve to the Rectus femoris.
- The articular branches to the knee-joint are three in number.
- One, a long slender filament, is derived from the nerve to the Vastus lateralis; it penetrates the capsule of the joint on its anterior aspect.
- Another, derived from the nerve to the Vastus medialis, can usually be traced downward on the surface of this muscle to near the joint; it then penetrates the muscular fibers, and accompanies the articular branch of the highest genicular artery, pierces the medial side of the articular capsule, and supplies the synovial membrane.
- The third branch is derived from the nerve to the Vastus intermedius.
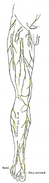
Additional images[]
External links[]
- GPnotebook -510001146
- Duke Orthopedics femoral_nerve
- MedlinePlus Encylopedia 000687 - "Femoral nerve dysfunction" (includes illustration)
- SUNY Labs 40:17-0202 - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Nerves of the Lumbar Plexus"
- Cross section at UV pembody/body15a
- Memorial University of Newfoundland - Anatomy at MUN nerve/lumbnerv
- Cross section at UV pelvis/pelvis-e12-15
- Anatomy at Dartmouth arteries-nerves%20LE/nerves1
- Diagram at nysora.com
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained herein may be outdated. Please edit the article if this is the case, and feel free to remove this notice when it is no longer relevant.
lumbar plexus: iliohypogastric - ilioinguinal - genitofemoral (femoral branch/lumboinguinal, genital branch) - lateral cutaneous of thigh (patellar) - obturator (anterior, cutaneous, posterior, accessory) - femoral (anterior cutaneous branches, saphenous)
sacral/coccygeal plexus: to quadratus femoris - to obturator internus - to the piriformis - superior gluteal - inferior gluteal - posterior cutaneous of thigh (inferior cluneal, perineal branches)
sciatic: tibial (medial sural cutaneous, sural, medial calcaneal, medial plantar, lateral plantar) - common fibular (lateral sural cutaneous, deep fibular, superficial fibular, medial dorsal cutaneous, intermediate dorsal cutaneous)
pudendal plexus: perforating cutaneous - pudendal (dorsal of the penis/clitoris, inferior anal, perineal and posterior scrotal/labial) - anococcygeal
- de:Nervus femoralis]]
- fr:Nerf fémoral]]
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |