Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)

Camillo Golgi, 1906.
Camillo Golgi (July 7, 1843 – January 21, 1926) was an Italian physician and scientist.
Golgi was born in Corteno, province of Brescia, Italy. His father was a physician and district medical officer. Golgi studied medicine at University of Pavia, where he worked in the experimental pathology laboratory under Giulio Bizzozero, who elucidated the properties of bone marrow. He graduated in 1865.
He spent much of his career studying the central nervous system. Tissue staining techniques in the latter half of the 19th century were inadequate for studying nervous tissue. While working as chief medical officer in a psychiatric hospital, he experimented with metal impregnation of nervous tissue, using mainly silver (silver staining). He discovered a method of staining nervous tissue which would stain a limited number of cells at random, in their entirety. This enabled him to view the paths of nerve cells in the brain for the first time. He called his discovery the "black reaction" (in Italian, reazione nera), which later received his name (Golgi's method) or Golgi stain. The reason for the random staining is still not understood.
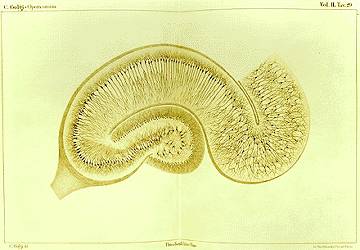
Drawing by Camillo Golgi of a hippocampus stained with the silver nitrate method
The black reaction consisted in fixing silver chromate particles to the neurilemma (the neuron membrane) by reacting silver nitrate with potassium dichromate. This resulted in a stark black deposit on the soma as well as on the axon and all dendrites, providing an exceedingly clear and well contrasted picture of neuron against a yellow background. The ability to visualize separate neurons led to the eventual acceptance of the neuron doctrine.
In addition to this discovery, Golgi discovered a tendon sensory organ that bears his name (Golgi receptor). He studied the life cycle of Plasmodium falciparum and related the timing of fevers seen in malaria with the life cycle of this organism. Using his staining technique, Golgi identified the intracellular reticular apparatus in 1898 which bears his name, the Golgi apparatus.
In renal physiology Golgi is renown for being the first to show that the distal tubulus of the nephron returns to its originating glomerulus a finding that he published in 1889 (Golgi, C. Annotazioni intorno alli'Istologia dei reni dell'uomo e di altri mammifieri e sull'istogenesi dei canalicoli oriniferi. Rendiconti R. Acad. Lincei 5: 545-557, 1889.).
Golgi, together with Santiago Ramón y Cajal, received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1906 for his studies of the structure of the nervous system.
Golgi died in Pavia, Italy, in January 1926.
External links[]
Nobel Laureates
in Physiology or Medicine |
|---|
|
Emil Behring (1901) • Ronald Ross (1902) • Niels Finsen (1903) • Ivan Pavlov (1904) • Robert Koch (1905) • Camillo Golgi / Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1906) • Alphonse Laveran (1907) • Ilya Mechnikov / Paul Ehrlich (1908) • Emil Kocher (1909) • Albrecht Kossel (1910) • Allvar Gullstrand (1911) • Alexis Carrel (1912) • Charles Robert Richet (1913) • Robert Bárány (1914) • Jules Bordet (1919) • August Krogh (1920) • Archibald Hill / Otto Meyerhof (1922) • Frederick Banting / John Macleod (1923) • Willem Einthoven (1924) |
|
Complete roster | (1901-1925) | (1926-1950) | (1951-1975) | (1976-2000) | (2001-2025) |
de:Camillo Golgi
es:Camillo Golgi
eu:Camillo Golgi
fr:Camillo Golgi
id:Camillo Golgi
sw:Camillo Golgi
la:Camillus Golgi
nl:Camillo Golgi
no:Camillo Golgi
pt:Camillo Golgi
fi:Camillo Golgi
sv:Camillo Golgi
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |