Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Cognitive Psychology: Attention · Decision making · Learning · Judgement · Memory · Motivation · Perception · Reasoning · Thinking - Cognitive processes Cognition - Outline Index
The same color illusion — also known as Adelson’s checker shadow illusion, checker shadow illusion and checker shadow — is an optical illusion published by Edward H. Adelson in 1995.[1] The squares A and B on the illusion are of the same color (or shade), although they seem to be different.
"When interpreted as a 3-dimensional scene, our visual system immediately estimates a lighting vector and uses this to judge the property of the material."[2]
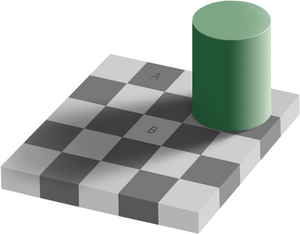
Squares A and B have the same color.
The image below proves that the squares A and B have the same color.
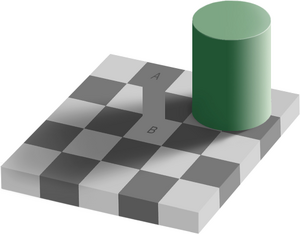
A rectangle of the same color has been drawn connecting the two squares.
As a further example, the two "A"s are both the same color and do not change. The shadow is removed in two frames, and the colors of the chess board are reversed.
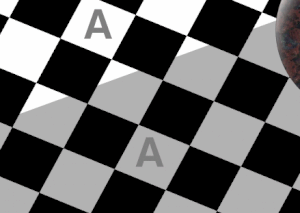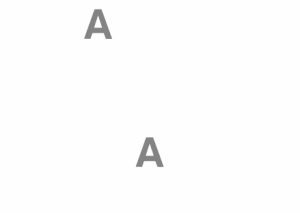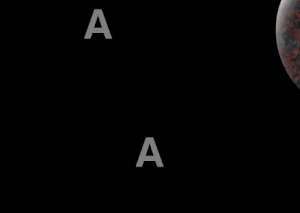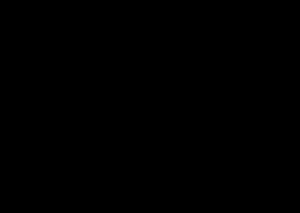
The two A's have the same color.
See also[]
References[]
- ↑ Adelson, Edward H. (2005). Checkershadow Illusion. URL accessed on 2007-04-21.
- ↑ michaelbach.de. URL accessed on 2006-06-10.
External links[]
- fr:Échiquier d'Adelson
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |