(Created page with "{{bioPsy}} {{Refimprove|date=December 2008}} thumb|right|"Views of a Fetus in the Womb", [[Leonardo da Vinci, ca. 1510-1512.]]...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{bioPsy}} |
{{bioPsy}} |
||
| + | |||
| − | {{Refimprove|date=December 2008}} |
||
[[Image:Views of a Foetus in the Womb.jpg|thumb|right|"Views of a Fetus in the Womb", [[Leonardo da Vinci]], ca. [[1510]]-[[1512]].]] |
[[Image:Views of a Foetus in the Womb.jpg|thumb|right|"Views of a Fetus in the Womb", [[Leonardo da Vinci]], ca. [[1510]]-[[1512]].]] |
||
| + | |||
| − | {{about|a medical term|the episode of the medical drama television series House|Fetal Position (House)}} |
||
'''Fetal position''' ([[British English]]: also foetal) is a medical term used to describe the [[position (Obstetrics)|position]]ing of the [[body]] of a prenatal [[fetus]] as it [[pregnancy|develops]]. In this position, the back is curved, the head is bowed, and the [[Limb (anatomy)|limbs]] are bent and drawn up to the torso. |
'''Fetal position''' ([[British English]]: also foetal) is a medical term used to describe the [[position (Obstetrics)|position]]ing of the [[body]] of a prenatal [[fetus]] as it [[pregnancy|develops]]. In this position, the back is curved, the head is bowed, and the [[Limb (anatomy)|limbs]] are bent and drawn up to the torso. |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
This position is used in the medical profession to minimize injury to the neck and chest. |
This position is used in the medical profession to minimize injury to the neck and chest. |
||
| + | ==In adulthood== |
||
Sometimes, when a person has suffered extreme [[physical trauma|physical]] or [[psychological trauma]] (including massive [[stress (medicine)|stress]]), they will assume the fetal position or a similar position in which the back is curved forward, the legs are brought up as tightly against the abdomen as possible, the head is bowed as close to the abdomen as possible, and the arms are wrapped around the [[head]] to prevent further [[Physical trauma|trauma]]. This position provides better protection to the [[brain]] and vital organs than simply lying spread out on the ground, so it is obvious as to why it is an instinctual reaction to extreme stress or trauma when the brain is no longer able to cope with the surrounding environment, and in essence "shuts down" temporarily. |
Sometimes, when a person has suffered extreme [[physical trauma|physical]] or [[psychological trauma]] (including massive [[stress (medicine)|stress]]), they will assume the fetal position or a similar position in which the back is curved forward, the legs are brought up as tightly against the abdomen as possible, the head is bowed as close to the abdomen as possible, and the arms are wrapped around the [[head]] to prevent further [[Physical trauma|trauma]]. This position provides better protection to the [[brain]] and vital organs than simply lying spread out on the ground, so it is obvious as to why it is an instinctual reaction to extreme stress or trauma when the brain is no longer able to cope with the surrounding environment, and in essence "shuts down" temporarily. |
||
| Line 25: | Line 26: | ||
Many baby [[mammal]]s, especially [[rodent]]s, remain in the fetal position well after being born. |
Many baby [[mammal]]s, especially [[rodent]]s, remain in the fetal position well after being born. |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== |
||
| + | *[[Human positions]] |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 00:36, 9 November 2011
Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
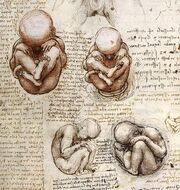
"Views of a Fetus in the Womb", Leonardo da Vinci, ca. 1510-1512.
Fetal position (British English: also foetal) is a medical term used to describe the positioning of the body of a prenatal fetus as it develops. In this position, the back is curved, the head is bowed, and the limbs are bent and drawn up to the torso.
This position is used in the medical profession to minimize injury to the neck and chest.
In adulthood
Sometimes, when a person has suffered extreme physical or psychological trauma (including massive stress), they will assume the fetal position or a similar position in which the back is curved forward, the legs are brought up as tightly against the abdomen as possible, the head is bowed as close to the abdomen as possible, and the arms are wrapped around the head to prevent further trauma. This position provides better protection to the brain and vital organs than simply lying spread out on the ground, so it is obvious as to why it is an instinctual reaction to extreme stress or trauma when the brain is no longer able to cope with the surrounding environment, and in essence "shuts down" temporarily.
The fetal position has been observed in drug addicts, who enter the position when experiencing withdrawal. Sufferers of anxiety are also known to assume the fetal position during panic attacks.
Many people assume this position when sleeping, especially when the body becomes cold.
A study by Professor Chris Idzikowski, director of the Sleep Assessment and Advisory Service found that people who sleep in the fetal position consistently tend to have a shy and sensitive personality. [1]
Assuming this position and playing dead is often recommended as a strategy to end a bear attack.[2]
Many baby mammals, especially rodents, remain in the fetal position well after being born.
See also
References
- ↑ includeonly>"Sleep position gives personality clue", BBC, 2003-09-16. Retrieved on 2009-05-10.
- ↑ "Bear Attacks Their Causes and Avoidance" by Stephen Herrero, pg 24 ISBN 0-941130-82-7
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |