Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
| Endolymph | ||
|---|---|---|
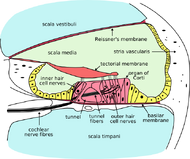
| Cross-section of cochlea. (Endolymph is located in the scala media - the light green region at the middle of the diagram.) | ||
| Latin | endolympha | |
| Gray's | subject #232 1051 | |
| System | ||
| MeSH | A12.207.270.517.324 | |
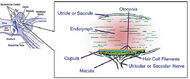
| illustration of otolith organs showing detail of utricle, ococonia, endolymph, cupula, macula, hair cell filaments, and saccular nerve | ||
Endolymph is the fluid contained in the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear.
It is also called Scarpa's fluid, after Antonio Scarpa.[1]
Composition[]
The main cation of this unique extracellular fluid is potassium, which is secreted from the stria vascularis. The high potassium content of the endolymph means that potassium, not sodium, is carried as the depolarizing electrical current in the hair cells. This is known as the mechano-electric transduction (MET) current.
Endolymph has a high positive charge (from 80-120 mV in the cochlea), mainly due to the presence of positively-charged amino acids. It is mainly this electrical gradient that allows potassium ions to flow into the negatively-charged hair cells during mechanical stimulation of the hair bundle. Because the hair cells are at a negative potential of about -50 mV, the electrical gradient from endolymph to hair cell is on the order of 150 mV, which is the largest electrical potential found in the body.
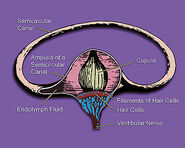
Role of endolymph in equilibrioception[]
In the vestibular system, equilibrioception is determined by the level of endolymph in the labyrinth
Pathology[]
Disruption of the endolymph due to jerky movements (like driving over bumps while riding in a car) can cause motion sickness[How to reference and link to summary or text]. A condition where the volume of the endolymph is greatly enlarged is called endolymphatic hydrops and has been linked to Ménière's disease[2].
See also[]
Additional images[]
References[]
External links[]
Sensory system: Auditory and Vestibular systems (TA A15.3, GA 10.1029) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer ear |
Pinna (Helix, Antihelix, Tragus, Antitragus, Incisura anterior auris, Earlobe) • Ear canal • Auricular muscles | ||||||||||||||
| Middle ear |
| ||||||||||||||
| Inner ear/ (membranous labyrinth, bony labyrinth) |
| ||||||||||||||
| {| class="navbox collapsible nowraplinks" style="margin:auto; " | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|}
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |