No edit summary |
(-L) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[Image:Ear-anatomy-text-small.png|thumb|250px|Anatomy of the human ear.]] |
[[Image:Ear-anatomy-text-small.png|thumb|250px|Anatomy of the human ear.]] |
||
| − | The '''ear canal''', or '''external auditory meatus''', is a tube running from the [[outer ear]] to the [[middle ear]]. The ear canal extends from the [[pinna]] to the [[eardrum]] and is about |
+ | The '''ear canal''', or '''external auditory meatus''', is a tube running from the [[outer ear]] to the [[middle ear]]. The ear canal extends from the [[pinna]] to the [[eardrum]] and is about 26mm in length and 7 mm in diameter. |
== Description and acoustic characteristics== |
== Description and acoustic characteristics== |
||
| − | The outer foundation of the ear canal is [[cartilage]] covered with [[skin]] that contains hairs and glands that secrete wax. The hairs and wax ([[cerumen]]) help prevent foreign bodies, such as |
+ | The outer foundation of the ear canal is [[cartilage]] covered with [[skin]] that contains hairs and glands that secrete wax. The hairs and wax ([[cerumen]]) help prevent foreign bodies, such as insects or dust, from entering the ear canal. |
| − | The ear canal protects the [[eardrum]] and acts as a [[resonator]], providing about 10 [[decibel|dB]] of gain to the eardrum at around 3,300 [[hertz|Hz]]. The net effect of the |
+ | The ear canal protects the [[eardrum]] and acts as a [[resonator]], providing about 10 [[decibel|dB]] of gain to the eardrum at around 3,300 [[hertz|Hz]]. The net effect of the head, [[pinna]], and ear canal is that sounds in the 2,000 to 4,000 Hz region are amplified by between 10 and 15 dB. Sensitivity to sounds is greatest in this [[frequency]] region and therefore excessive noise in this range is the most likely to cause hearing damage. |
The external auditory meatus is formed from the groove (cleft) of the first branchial arch. |
The external auditory meatus is formed from the groove (cleft) of the first branchial arch. |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Size and shape == |
== Size and shape == |
||
| − | The ear canal is approximately 26mm long and 7mm in diameter. Size and shape of the canal vary among individuals. This is an important factor to consider when fitting |
+ | The ear canal is approximately 26mm long and 7mm in diameter. Size and shape of the canal vary among individuals. This is an important factor to consider when fitting hearing protectors. |
| + | |||
| − | ==Disorders== |
||
| − | The ear canal, because of its relative exposure to the outside world, is a common victim of diseases and other disorders. Some disorders include: |
||
| − | * [[Otitis externa]] (swimmer's ear), bacteria-caused inflammation of the ear canal |
||
| − | * Contact [[dermititis]] of the ear canal |
||
| − | * Ear fungus |
||
| − | * Ear [[myiasis]], an extremely rare infestation of maggots |
||
| − | * Bone exposure, caused by the wearing away of skin in the canal |
||
| − | *[[Granuloma]], [[scar tissue]] usually caused by ear tubes |
||
| − | *[[Stenosis]], a gradual closing of the canal |
||
| − | *Foreign body in ear |
||
==Additional images== |
==Additional images== |
||
Revision as of 23:48, 7 December 2006
Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
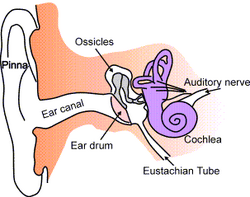
Anatomy of the human ear.
The ear canal, or external auditory meatus, is a tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about 26mm in length and 7 mm in diameter.
Description and acoustic characteristics
The outer foundation of the ear canal is cartilage covered with skin that contains hairs and glands that secrete wax. The hairs and wax (cerumen) help prevent foreign bodies, such as insects or dust, from entering the ear canal.
The ear canal protects the eardrum and acts as a resonator, providing about 10 dB of gain to the eardrum at around 3,300 Hz. The net effect of the head, pinna, and ear canal is that sounds in the 2,000 to 4,000 Hz region are amplified by between 10 and 15 dB. Sensitivity to sounds is greatest in this frequency region and therefore excessive noise in this range is the most likely to cause hearing damage.
The external auditory meatus is formed from the groove (cleft) of the first branchial arch.
Size and shape
The ear canal is approximately 26mm long and 7mm in diameter. Size and shape of the canal vary among individuals. This is an important factor to consider when fitting hearing protectors.
Additional images
References
Sensory system: Auditory and Vestibular systems (TA A15.3, GA 10.1029) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer ear |
Pinna (Helix, Antihelix, Tragus, Antitragus, Incisura anterior auris, Earlobe) • Ear canal • Auricular muscles | ||||||||||||||
| Middle ear |
| ||||||||||||||
| Inner ear/ (membranous labyrinth, bony labyrinth) |
| ||||||||||||||
| {| class="navbox collapsible nowraplinks" style="margin:auto; " | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|}
de:Gehörgang lt:Klausomoji landa nl:Gehoorgang fi:Korvakäytävä
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |