Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
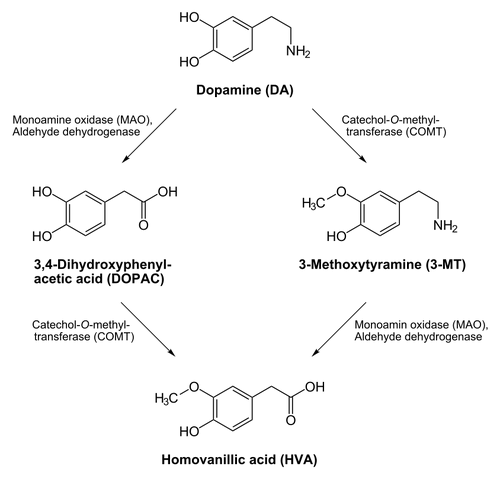
Dopamine metabolites are the products following the breakdown of Dopamine
Dopamine is inactivated by reuptake via the dopamine transporter, then enzymatic breakdown by catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) and monoamine oxidase (MAO). Dopamine that is not broken down by enzymes is repackaged into vesicles for reuse.
Dopamine may also simply diffuse away from the synapse, and help to regulate blood pressure.
DOPAC[]
DOPAC (dihydroxyphenylacetic acid) is a metabolite of dopamine. The dopaminergic pathway consists of the following:
----> via MAO -> '''DOPAC''' -> via COMT
/ \
'''Dopamine (DA)''' . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ---> '''homovanillic acid (HVA)'''
\ /
----> via COMT -> '''3-MT''' -> via MAO
One of the three direct products from the alteration of dopamine (DOPAC, 3-MT (3-methoxytyramine) and noradrenaline) DOPAC is an important metabolite when studying the behaviour of the dopaminergic system for multiple reasons; 3-MT is generally more difficult to assay alongside dopamine and by assessing all three metabolites (DOPAC, HVA and 3-MT) abnormalities in either COMT (catechol-O-methyl transferase) or MAO (monoamine oxidase) can be indirectly identified. This has large ramifications as COMT abnormalities are suspected in various neuropsychiatric diseases including schizophrenia.