No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{BioPsy}} |
{{BioPsy}} |
||
| + | {{Infobox Brain| |
||
| + | Name = Cerebral peduncle | |
||
| + | Latin = pedunculus cerebri | |
||
| + | GraySubject = 188 | |
||
| + | GrayPage = 800 | |
||
| + | Image = Gray689.png | |
||
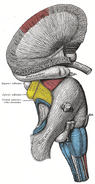
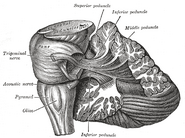
| + | Caption = Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Ventral view. ("Cerebral peduncle" visible in red at center-right.) | |
||
| + | Image2 = cn3nucleus.png | |
||
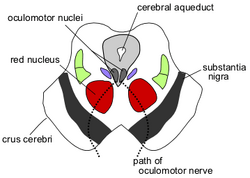
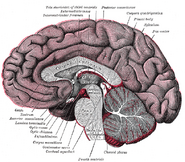
| + | Caption2 = Section through [[superior colliculus]] showing path of [[oculomotor nerve]]. (Crus cerebri labeled at lower left.) | |
||
| + | IsPartOf = | |
||
| + | Components = | |
||
| + | Artery = |
||
| + | Vein = | |
||
| + | BrainInfoType = hier | |
||
| + | BrainInfoNumber = 478 | |
||
| + | MeshName = Cerebral+Peduncle | |
||
| + | MeshNumber = A08.186.211.132.659 | |
||
| + | NeuroLex = Central peduncle |
||
| + | | NeuroLexID = birnlex_1202 | |
||
| + | DorlandsPre = p_10 | |
||
| + | DorlandsSuf = 12622555 | |
||
| + | }} |
||
| + | Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the [[cortex]], the [[spinal cord]] and the [[cerebellum]].<ref name="Saladin">{{citation| author=Saladin, Kenneth |title=Anatomy & Physiology The Unity of Form and Function |location=New York, NY |publisher=McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. |year=2010}}</ref> The '''cerebral peduncle''', by most classifications, is everything in the [[mesencephalon]] except the [[tectum]].{{Citation needed|date=May 2010}} The region includes the [[midbrain tegmentum]], [[crus cerebri]] and [[pretectum]]. By this definition, the cerebral peduncles are also known as the '''[[basis pedunculi]],''' while the large ventral bundle of efferent fibers is referred to as the '''[[crus cerebri]]''' or the '''[[pes pedunculi]]'''. There are numerous nerve tracts located within this section of the [[brainstem]]. Of note, in the ''cerebral peduncular loop'' fibers from motor areas of the brain project to the cerebral peduncle and then project to various [[thalamus|thalamic nuclei]]. |
||
| + | Important fibers running through the cerebral peduncles include the [[corticospinal tract]] and the [[corticobulbar tract]], among others. This area contains many nerve tracts conveying motor information to and from the brain to the rest of the body. |
||
| − | The '''cerebral peduncle''', by most classifications, is everything in the [[mesencephalon]] except the tectum. The region includes the [[midbrain tegmentum]], [[crus cerebri]], [[substantia nigra]] and [[pretectum]]. The peduncles are also known as the "crus cerebri". |
||
| + | ==Additional images== |
||
| − | In the ''cerebral peduncular loop'' fibers from motor areas of the brain project to the cerebral peduncle and then project to various [[thalamus|thalamic nuclei]]. |
||
| + | <gallery> |
||
| + | Image:Gray677.png|Scheme showing the connections of the several parts of the brain. |
||
| + | Image:Gray682.png|Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view. |
||
| + | Image:Gray683.png|Dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view. |
||
| + | Image:Gray684.png|Deep dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view. |
||
| + | Image:Gray705.png|Dissection showing the projection fibers of the cerebellum. |
||
| + | Image:Gray720.png|Median sagittal section of brain. |
||
| + | Image:Gray773.png|The left optic nerve and the optic tracts. |
||
| + | Image:Gray792.png|Upper part of medulla spinalis and hind- and mid-brains; posterior aspect, exposed in situ. |
||
| + | Image:Human brainstem anterior view 2 description.JPG|Human brainstem anterior view |
||
| + | File:Slide6dd.JPG|Cerebral peduncle |
||
| + | File:Slide2cuc.JPG|Cerebrum. Deep dissection. Inferior dissection. |
||
| + | </gallery> |
||
| + | ==See also== |
||
| − | + | * [[list of regions in the human brain|Regions in the human brain]] |
|
| + | |||
| + | ==References== |
||
| + | {{Reflist}} |
||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== |
||
| + | * [http://thalamus.wustl.edu/course/cor6.gif Diagram] |
||
| + | * [http://mail.biocfarm.unibo.it/aunsnc/3dobjl7.html Diagram] |
||
| + | * [http://137.204.242.20/aunsnc/pictefl27.html Photo] |
||
| + | * [https://www.neuinfo.org/mynif/search.php?q=Cerebral%20Peduncle&t=data&s=cover&b=0&r=20 NIF Search - Cerebral Peduncle] via the [[Neuroscience Information Framework]] |
||
| − | {{neuroscience-stub}} |
||
{{Mesencephalon}} |
{{Mesencephalon}} |
||
| + | |||
[[Category:Cerebrum]] |
[[Category:Cerebrum]] |
||
| + | |||
{{enWP|Cerebral_peduncle}} |
{{enWP|Cerebral_peduncle}} |
||
Latest revision as of 00:32, 30 May 2013
Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
| Brain: Cerebral peduncle | ||
|---|---|---|
| Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Ventral view. ("Cerebral peduncle" visible in red at center-right.) | ||
| Section through superior colliculus showing path of oculomotor nerve. (Crus cerebri labeled at lower left.) | ||
| Latin | pedunculus cerebri | |
| Gray's | subject #188 800 | |
| Part of | ||
| Components | ||
| Artery | Vein = | |
| Vein | {{{Vein}}} | |
| BrainInfo/UW | hier-478 | |
| MeSH | A08.186.211.132.659 | |
Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the cortex, the spinal cord and the cerebellum.[1] The cerebral peduncle, by most classifications, is everything in the mesencephalon except the tectum.[citation needed] The region includes the midbrain tegmentum, crus cerebri and pretectum. By this definition, the cerebral peduncles are also known as the basis pedunculi, while the large ventral bundle of efferent fibers is referred to as the crus cerebri or the pes pedunculi. There are numerous nerve tracts located within this section of the brainstem. Of note, in the cerebral peduncular loop fibers from motor areas of the brain project to the cerebral peduncle and then project to various thalamic nuclei.
Important fibers running through the cerebral peduncles include the corticospinal tract and the corticobulbar tract, among others. This area contains many nerve tracts conveying motor information to and from the brain to the rest of the body.
Additional images
See also
References
- ↑ Saladin, Kenneth (2010), Anatomy & Physiology The Unity of Form and Function, New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
External links
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |