(New page: {{BioPsy}} thumb|[[Acetylcholine]] thumb|[[Acetylcholinesterase]] An '''Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor''' or ''...) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
| + | {{Enzyme inhibition}} |
||
| − | |||
[[Category:Anticholinesterases|*]] |
[[Category:Anticholinesterases|*]] |
||
Revision as of 10:16, 10 April 2007
Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
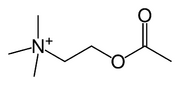
An Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor or Anti-cholinesterase is a chemical that inhibits the cholinesterase enzyme from breaking down acetylcholine, so increasing both the level and duration of action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Uses
Anticholinesterases occur naturally as venoms and poisons, are used as weapons in the form of nerve agents, and are used medicinally to treat diseases such as myasthenia gravis and Alzheimer's disease, and as an antidote to anticholinergic poisoning. In myasthenia gravis, they are used to increase neuromuscular transmission.
Examples
reversible inhibitor
Compounds which function as reversible competitive or noncompetitive inhibitors of cholinesterase are those most likely to have therapeutic uses. These include:
- Organophosphates
- metrifonate
- Carbamates
- physostigmine
- neostigmine
- pyridostigmine
- ambenonium
- demarcarium
- rivastigmine
- Phenanthrine derivatives
- Piperidines
- donepezil, also known as E2020
- Tacrine, also known as tetrahydroaminoacridine (THA')
- Edrophonium
quasi-irreversible inhibitor
Compounds which function as quasi-irreversible inhibitors of cholinesterase are those most likely to have use as chemical weapons or pesticides. These include:
- Organophosphates
- Carbamates
- aldicarb
- bendiocarb
- bufencarb
- carbaryl
- carbendazim
- carbetamide
- carbofuran
- chlorbufam
- chloropropham
- ethiofencarb
- formetanate
- methiocarb
- methomyl
- oxamyl
- phenmedipham
- pinmicarb
- pirimicarb
- propamocarb
- propham
- propoxur
Effects
Some major effects of anticholinesterases:
- Actions on the autonomic nervous system, that is parasympathetic nervous system will cause bradycardia, hypotension, hypersecretion, bronchoconstriction, GIT hypermotility, and decrease intraocular pressure.
- SLUD syndrome.
- Actions on the neuromuscular junction will result in prolonged muscle contraction.
See also
External links
Pharmacology: enzyme inhibition | |
|---|---|
| Class |
Competitive inhibition - Uncompetitive inhibition - Non-competitive inhibition - Suicide inhibition - Mixed inhibition |
| Substrate |
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors - Aromatase inhibitors - Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - Integrase inhibitor - Kinase inhibitors - Lipoxygenase inhibitor - Monoamine oxidase inhibitors - Reverse transcriptase inhibitors - Phosphodiesterase inhibitors - Protease inhibitors (ACE inhibitor, Trypsin inhibitor) |
Template:Enwp